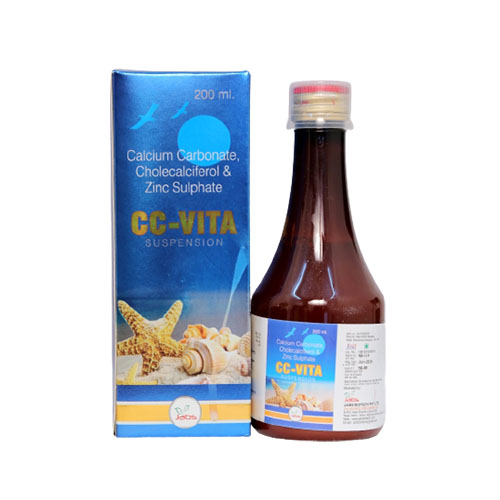
CC-VITA consists of Calcium Carbonate, Cholecalciferol & Zinc Suspension that is used in various kinds of vitamins and minerals deficiencies. Along with treating the nutritional deficiencies, they are also prescribed for some other conditions like osteoporosis. Calcitriol is very useful for the body as it helps the body to absorb Calcium Carbonate and it also supports the muscle’s growth so that they don’t break easily. Zinc is also very good for building and maintaining good bone health.
Zinc is important for maintaining the structure and integrity of cell membranes that are important in the overall body function. It also plays an important role in the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. It is also a cofactor in a range of biochemical processes, including the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and proteins. Calcium Carbonate, Cholecalciferol & Zinc Suspension is also prescribed in pregnancy and lactation.
Uses of Calcium Carbonate, Cholecalciferol & Zinc Suspension
- The risk of osteoporotic/osteopenic fractures is reduced.
- It significantly increases bone mineral density.
- Also reduces the increased blood pressure during the second half of pregnancy.
- The intestinal absorption and utilization of calcium and phosphorus are increased.
- Bone density is also increased in those individuals who are having osteoporosis.
Side Effects
Calcium Carbonate, Cholecalciferol & Zinc Suspension may cause some side effects which aren’t major in nature as they are likely to go away with time once the body starts to adjust itself with time.
- Nausea/ vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Unusual weight loss
Directions For Use
- Take this suspension as per the prescription of the doctor concerned that is looking after the treatment.
- Usually, this is taken two times a day after having a meal.
- The individual must try to take a healthy diet along with this medicine so that the dependency on this medicine can be reduced accordingly.
- It is advised to complete the whole treatment that is suggested by the doctor so that all the proper benefits can be taken by using this medicine.
- The dose adjustment will be done only by the doctor and it is not suggested to be done by the individual by himself.
Safety Precautions
- Before starting the treatment with this medicine let the doctor know if you the individual is having any kind of allergies related to this medicine or to any other one.
- Let the doctor know if the individual is having any liver or kidney issues with him.
- Special attention may be needed if the patient had any problems related to heart/blood vessel disease, kidney stones, certain immune system disorders, certain bowel diseases.
- Let the doctor know if the woman taking this medicine is pregnant or breastfeeding.
- It is advised to not consume alcohol while using this medication as it can cause some problems in that case.
Contact For Calcium Carbonate, Cholecalciferol & Zinc Suspension Manufacturing And Supply
Jabs Biotech is a well-known Pharma company that is working very well to offer its WHO, GMP certified pharma products to all those who are linked with it. We are conceived as the top Calcium Carbonate, Cholecalciferol & Zinc Suspension manufacturer, and supplier in India. The firm is also offering Calcium Carbonate, Cholecalciferol & Zinc Suspension PCD Pharma Franchise in India with exclusive and complete monopoly rights. All the orders are delivered by us within the stipulated time period so that the linked party doesn’t face any issues.











 call us
call us whatsapp
whatsapp Contact Us
Contact Us